The developers behind the notorious Raccoon Stealer malware have reemerged after a six-month absence from hacker forums, promoting an updated 2.3.0 version of their malware to cybercriminals.
Since its introduction in 2019, Raccoon has become one of the most prominent and prolific information-stealing malware families, sold through a subscription model at $200 per month to threat actors.
Raccoon Stealer is capable of extracting data from over 60 applications, including user login credentials, credit card details, browsing history, cookies, and cryptocurrency wallet accounts.
In October 2022, the project faced a significant setback when Mark Sokolovsky, the primary developer of the malware, was arrested in the Netherlands, and the FBI dismantled the malware’s service infrastructure.
The Return of Raccoon Stealer
In a recent post, first identified by VX-Underground, the current authors of the malware notified the cybercriminal community of their return, revealing that they have been “working tirelessly” to develop new features intended to enhance the user experience of their malicious clientele. These updates were informed by user feedback, specific requests, and prevailing cyber crime trends—with the goal of maintaining Raccoon’s standing in the top echelon of information stealers.
According to a numerous reports, Raccoon 2.3.0 has incorporated several significant user-friendly and operational security enhancements. These improvements are designed to simplify the malware’s use for less technically savvy threat actors and to make tracing by researchers and law enforcement more challenging.
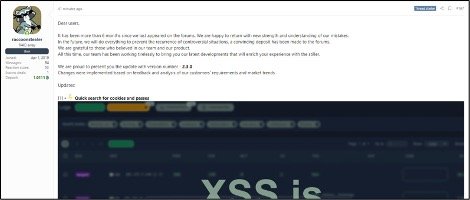
Announcement of Raccoon v2.3.0 on hacker forums
Source: Cyberint
Information-stealing malware like Raccoon poses a significant and extensive threat to both individual users and businesses. Its pervasive use by cybercriminals ensures that malicious payloads are delivered through numerous channels, targeting a vast and diverse audience. Moreover, since this malware can also steal session cookies, it may enable threat actors to bypass multi-factor authentication safeguards, thereby breaching corporate networks. Once inside, attackers can deploy various offensive strategies, including data theft, ransomware attacks, BEC scams, and cyber-espionage tactics.
The Ongoing Threat and New Features
Quick Search for Cookies and Passes:
The updated Raccoon admin panel introduces an innovative way to search for URLs. This improvement enables threat actors to swiftly find specific links in large datasets, even when dealing with millions of documents and thousands of disparate links—a notable enhancement in efficiency and convenience for users of this malware.
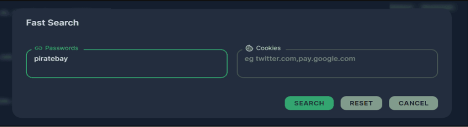
Raccoon Stealer Quick Search Module
Source: Cyberint
Automatic Bot Blocking and Panel Display:
Raccoon now includes a system designed to detect anomalous activity patterns, such as repeated accesses from the same IP address or range. Upon detecting such activity, this system automatically deletes the associated records and updates the client pads, thereby thwarting security tools relying on automation and bots for malware detection.

Raccoon Stealer Dashboard with Bot Blocking and Panel Display
Source: Cyberint
Legend: Green Smiley = Activity of the IP is normal. Red Smiley = High probability that bots or other automated systems created or actively used the log.
Reporting System:
This new feature blocks IP addresses typically used by security practitioners’ crawlers and bots to monitor Raccoon’s network traffic.
Racoon Stealer Reporting System per IP Address
Source: Cyberint
Log Statistics:
This feature enables threat actors to review detailed statistics about their activities, including a geographic breakdown of compromised systems, reminiscent of functionalities in earlier versions of the malware.

Raccoon Stealer Behavior and Capabilities
Raccoon targets a comprehensive range of applications, employing specialized techniques to extract and harvest data. Raccoon’s modus operandi for data extraction from targeted applications generally involves the following steps:
- Extract the file from the targeted application that contains sensitive data.
- Copy this file to a designated folder (usually %Temp%).
- Generate a text file within the targeted application’s directory, which contains the stolen data.
- To decrypt credentials from applications, Raccoon retrieves and downloads the necessary DLLs associated with these applications.
Based on Proficio’s research, as of 08/15/2023, there are 9,515,216 Raccoon stealer findings listed throughout the dark, deep and surface internet.
Sample Raccoon Malware Logs:
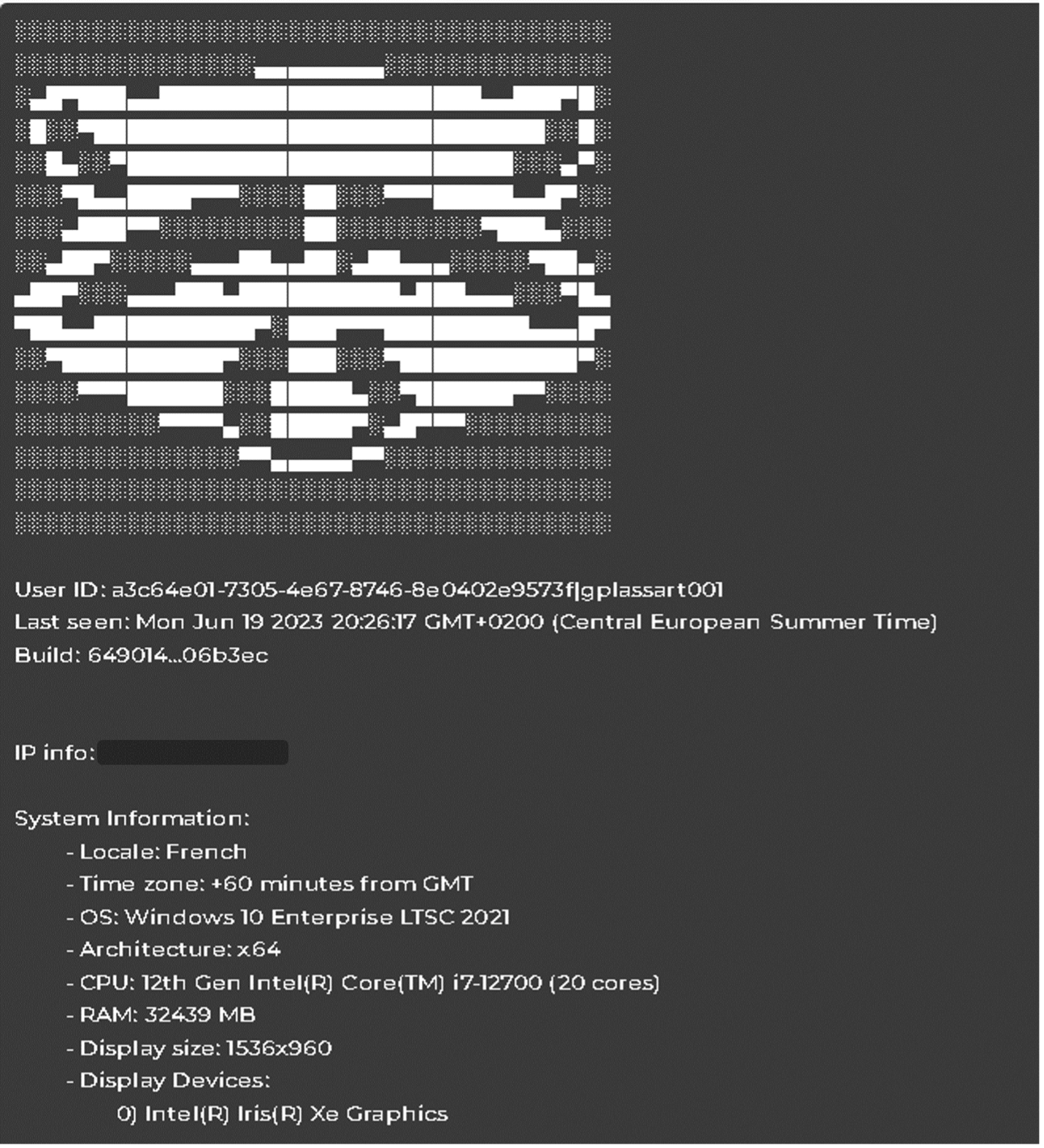
Source: Proficio Cyber Exposure Monitoring Platform
Targeted Applications Include
Browsers:
| Google Chrome | Comodo Dragon | Amigo |
| Orbitum | Bromium | Nichrome |
| RockMelt | 360Browser | Vivaldi |
| Opera | Sputnik | Kometa |
| Uran | QIP Surf | Epic Privacy |
| CocCoc | CentBrowser | 7Star |
| Elements | TorBro | Suhba |
| Safer Browser | Mustang | Superbird |
| Chedot | Torch | Internet Explorer |
| Microsoft Edge | Firefox | WaterFox |
| SeaMonkey | PaleMoon | – |
Email Clients:
- ThunderBird
- Outlook
- Foxmail
Cryptocurrency Wallets:
- Electrum
- Ethereum
- Exodus
- Jaxx
- Monero
- Bither
Racoon Stealer Detection Steps:
- Monitor System Behavior: Regularly check for unusual system behavior, such as unexpected data flows or high CPU usage when no major tasks are running, which may indicate malware activity.
- Antivirus Scans: Conduct frequent and thorough scans using updated antivirus software that can detect known variants of Raccoon and similar malware.
- Check for Unusual Network Traffic: Continuously monitor network traffic for uncommon data exfiltration attempts or communication with known malicious IP addresses.
- Inspect System Logs: Review system and security logs for irregularities or signs of intrusion.
Remediation Steps:
- Isolate Infected Systems: Immediately quarantine affected systems from the network to prevent the malware from spreading.
- Remove Malware: Use reputable antivirus or antimalware tools to clean the infected systems.
- Change All Passwords: After removing the malware, change all passwords, starting with the most sensitive accounts.
- Update Software: Ensure that all systems are running the latest versions of operating systems and applications, which include security patches.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): To add an extra layer of security, enable MFA on all possible accounts.
- Review Permissions and Access: Conduct a comprehensive audit of user permissions and restrict privileges to the minimum necessary for each role.
Defensive Measures:
- Use Password Managers: Employ password managers as opposed to saving credentials within browsers.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication: Activate MFA across all accounts as a robust preventative measure.
- Exercise Caution with Downloads: Avoid downloading executable files from questionable websites, even when directed to these sites from seemingly trustworthy platforms like Google Ads, YouTube videos, or Facebook posts.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Keep operating systems and all software up to date with the latest security patches.
- Educate Employees and Users: Regularly educate and train staff or users about the risks of phishing scams and how to recognize potential malware lures.
Note:
These measures are not exhaustive but represent essential steps in detecting, remediating, and defending against threats like the Raccoon Stealer malware.
Conclusion:
The resurgence of the Raccoon Stealer malware, marked by the release of version 2.3.0, underscores the persistent threat posed by sophisticated cybercriminal operations. After a hiatus following the arrest of its primary developer, Mark Sokolovsky, and the dismantling of its infrastructure by law enforcement agencies, the creators of Raccoon have returned with renewed vigor.
Their latest iteration, heralded on hacker forums, boasts enhanced features aimed at facilitating ease of use for cybercriminals while simultaneously thwarting detection efforts by security researchers and law enforcement. With an expanded repertoire of applications targeted for data extraction and the ability to bypass security measures like multi-factor authentication, Raccoon remains a formidable tool in the arsenal of cyber adversaries.
In the face of this ongoing threat, it is imperative for individuals and organizations to remain vigilant. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including regular system monitoring, antivirus scans, network traffic analysis, and user education, is crucial to mitigate the risks posed by malware. By staying informed and proactive, users can fortify their defenses and minimize the potential impact of malicious activities orchestrated by threat actors.
As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, the battle against malware like Raccoon Stealer requires collective effort and constant adaptation. Only through concerted action and a commitment to cybersecurity best practices can we effectively safeguard our digital assets and preserve the integrity of our online environments.
Article References:
https://twitter.com/vxunderground/status/1691175828607111171
https://cyberint.com/blog/financial-services/raccoon-stealer/
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/raccoon-stealer-malware-returns-with-new-stealthier-version/
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/ukrainian-charged-for-operating-raccoon-stealer-malware-service/